#3 Digital Creative Abilities
The third issue our newsletter looks at one of the core assets of our project: the Digital Creative Abilities, a set of core competencies need to facilitate future digital transformation processes.

Digital Creativity for developing Digital Maturity Future Skills (DC4DM Project) is an EU-funded initiative that brings together partners from Italy, France and Portugal in an effort to foster a new culture of creativity in digital innovation.
Over the next two years, the team consisting of design, digital and innovation specialists from Politecnico Di Milano, Startup Madeira, Mines Saint Etienne, Universidade da Madeira, and Université Jean Monnet Saint Etienne will create a new programme for helping students and startups to put creativity at the service of new digital technologies. Our goal is to create and implement a human-centred design model to facilitate and guide the ever-evolving process of digitalisation through the enhancement of creative skills.
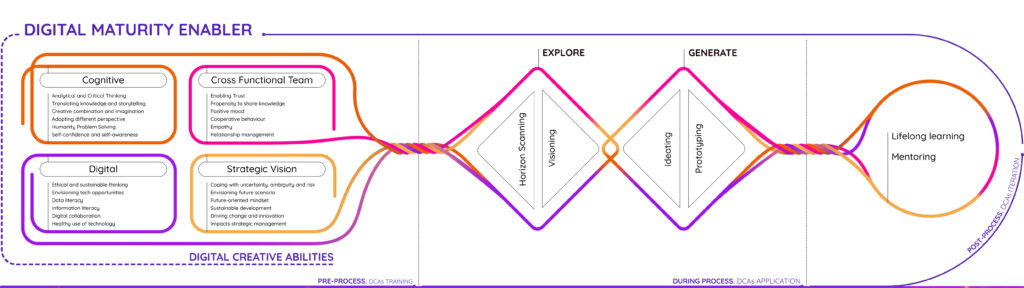
The Digital Maturity Enabler
To achieve digital transformation, organisations need a guide—a digitally wise person who is able to be an interpreter of the digital landscape.
This figure takes the name of a Digital Maturity Enabler: a person who, owning specific creative digital skills (DCA), is able to extract value in a creative way from what the technological landscape offers, by responding to human needs.
A DMEnabler is a person with either a design, engineering or managerial background who is able to consciously apply new technologies being well aware of their potential social and environmental impacts; share ideas and specific knowledge within cross-functional teams; a person with a strong future- oriented mindset and use foresight tools and methods to create original scenarios.
Hence, the need to up-skill future generations to proactively face the ongoing radical changes and deal with such ever-emerging digital challenges to start moving towards a collective preferable future.
Digital Creativity for Digital Maturity model (DC4DM)
In order to help develop the next generation of Digital Maturity Enablers, innovative educational models must be built and applied.
They have to provide upcoming generations with a radically new skill set to enhance their creative abilities enabling them to spot and exploit the viable potentialities of emerging technologies.
In this extremely complex contemporary scenario, human creativity is notably acknowledged as an essential ability to help people navigate successfully in this digitally enabled world and empower them to strategically unlock the multiple opportunities brought by emerging technologies (Bruno & Canina, 2019).
The DC4DM model aims to provide the fundamental competencies needed to thrive in a continuously advancing digital landscape and reach Digital Maturity. Digital talents have to be prepared to face the diversity of uncertain futures, anticipate possible scenarios, and take full advantage of the innovation capacity of digital technologies.
The model has, therefore, the aim to enable and empower learners in:
acquiring competencies and mindset to understand the potentialities of digital technologies and apply them to design digital solutions with a
human-centred approach;
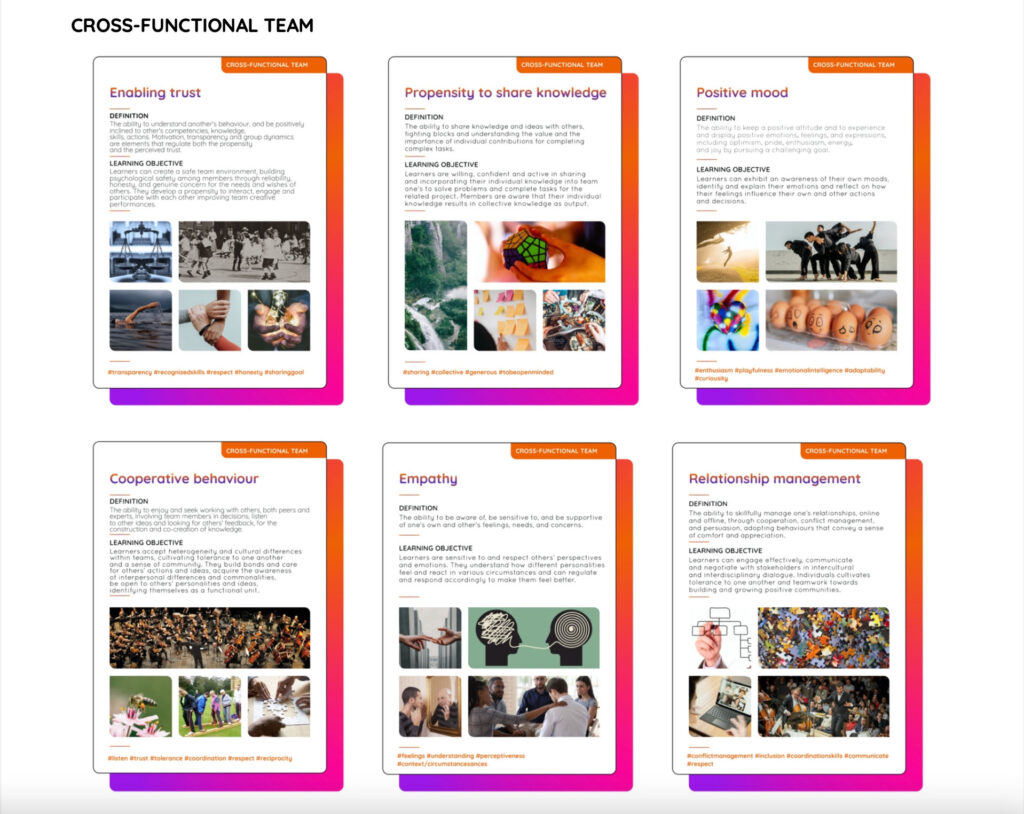
developing individual abilities of creative self-enhancement and a digitally-minded culture, as well as the team’s ability to communicate and share knowledge with others with a different background;
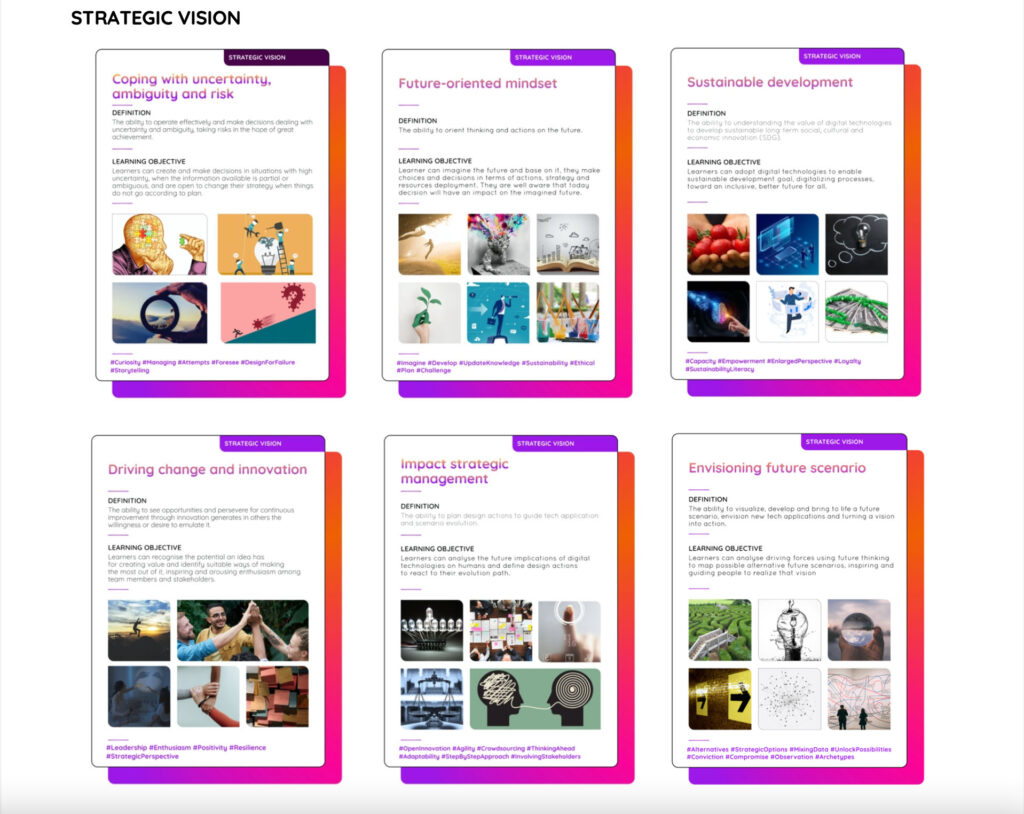
acquiring skills in future and anticipatory thinking, developing a mindset that can generate a long-term strategic vision and help companies face complex challenges by envisioning future scenarios.
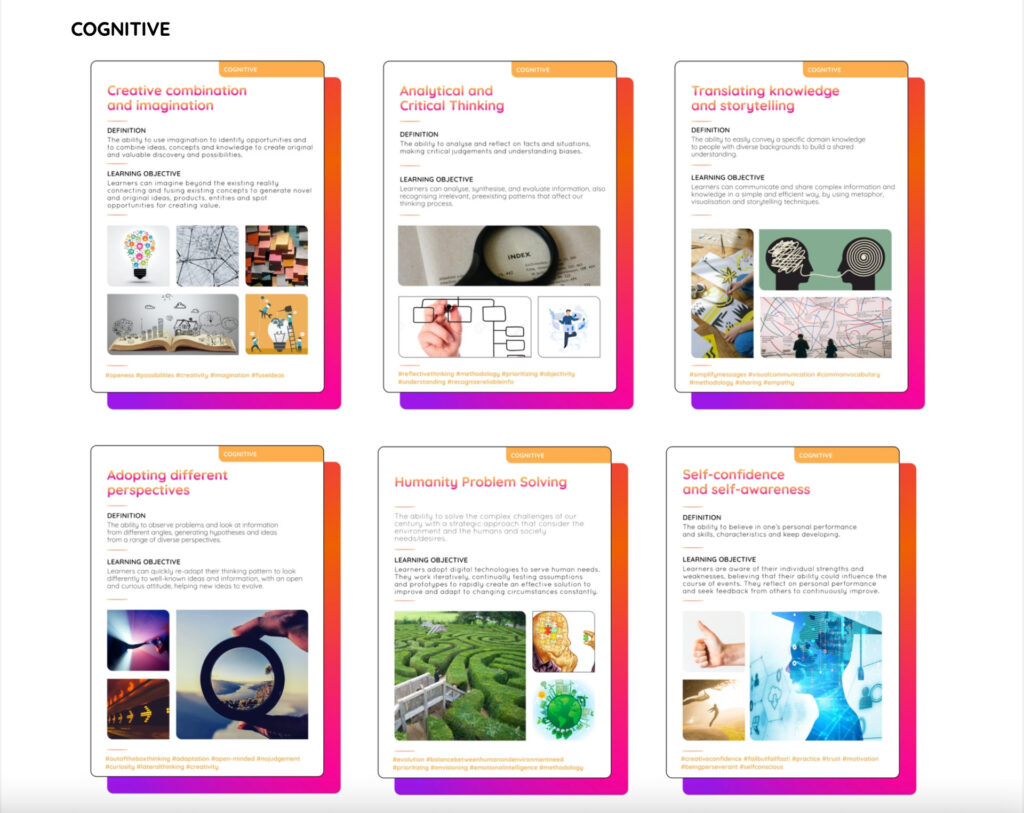
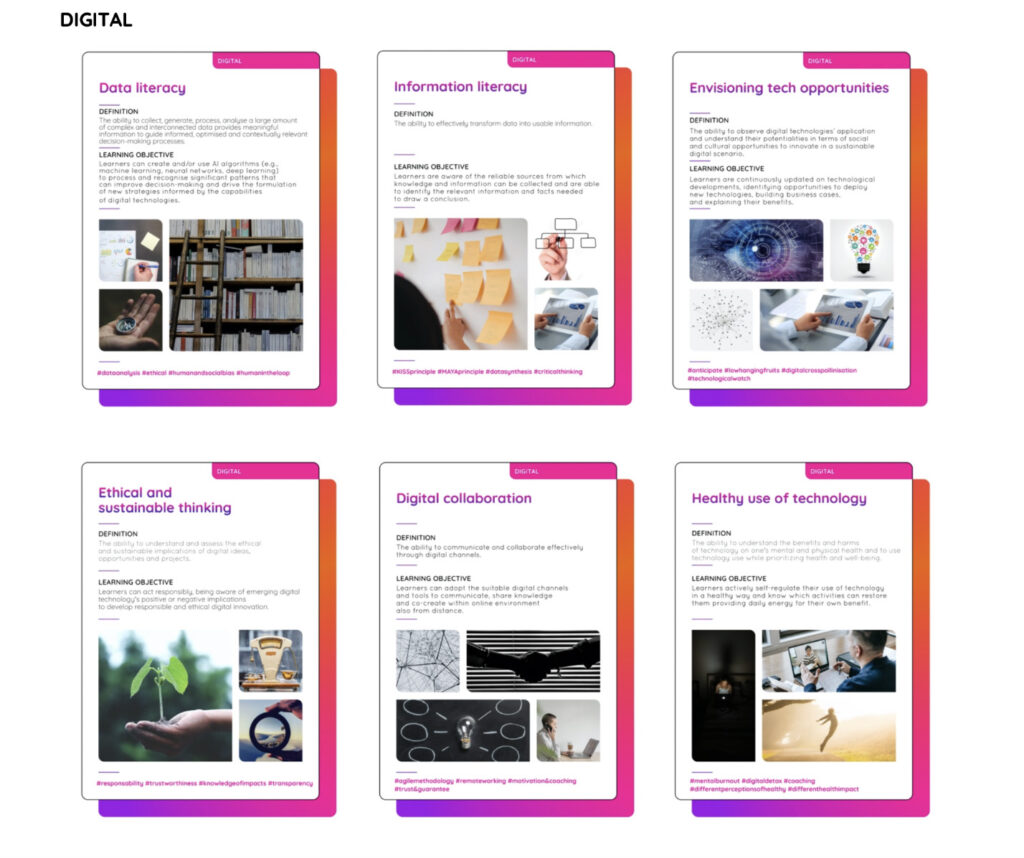
Digital Creativity Abilities (DCAs)
The DC4DM model integrates a set of skills and attitudes identified as in line with Digitally Mature companies’ needs and key practices and, therefore, relevant for training future digital talents.
These fundamental skills can be defined as digital creative abilities (DCAs), that allow individuals to express their full creative potential.
DCAs have been identified, integrated, and transformed by analysing and comparing the 4 main competence Frameworks outlined by both companies and policymakers.
These abilities synthesise the three main objectives of the DC4DM model according to which students need to acquire competencies to:
understand technology’s potentialities and apply them in relevant digital solutions employing a human-centred design approach;
work smoothly in a cross-functional team, being able to communicate effectively with people coming from different fields and developing a digitally- minded and creative culture;
anticipate possible future scenarios to define long-term strategies for identifying the opportunities and handling the risks that digital technologies might generate and tackle complexity and uncertainty.
They comprise not only a broad range of skills (cognitive, social, emotional, etc.) but also disciplinary and procedural knowledge and attitudes and values that guide how knowledge and skills are used to face challenges.
The DCAs are clustered in 4 main dimensions:
Cognitive
Digital
Cross-functional team
Strategic vision